Services
Non-Cancerous Fibroid Management
Specialized Treatments Offered
In vitro fertilization (IVF)
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
Laparoscopic surgery
Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas, are benign (non-cancerous) growths that develop in or on the uterus. These fibroids can vary in size and number, and while many women with fibroids have no symptoms, others may experience significant discomfort or complications. Fibroids are common, affecting up to 70-80% of women by the age of 50, and their management depends on various factors, including the size, location, and severity of symptoms.
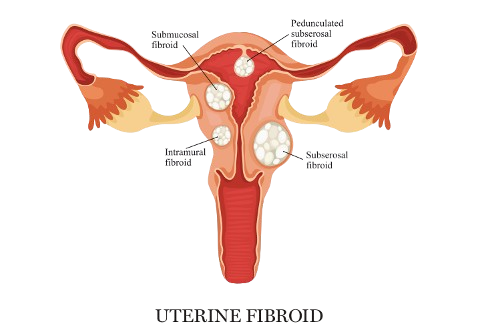
Types of Fibroids
Fibroids can develop in different parts of the uterus, affecting the treatment approach:
Intramural Fibroids: These develop within the muscle wall of the uterus.
Submucosal Fibroids: These grow just underneath the uterine lining and may cause heavy bleeding and fertility issues.
Subserosal Fibroids: These grow on the outer wall of the uterus and may cause pressure on surrounding organs, like the bladder or rectum.
Pedunculated Fibroids: These are attached to the uterus by a stalk (peduncle) and can occur on the inside or outside of the uterus.
Symptoms of Fibroids
While many women with fibroids do not experience symptoms, those who do may present with:
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia): Prolonged periods or unusually heavy bleeding during menstruation.
Pelvic Pain or Pressure: Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, which can be dull or sharp, and may worsen during menstruation.
Frequent Urination: Pressure on the bladder caused by fibroids.
Constipation: Pressure on the rectum.
Back Pain: Persistent pain in the lower back.
Pain During Intercourse (Dyspareunia): Discomfort during or after sexual activity.
Reproductive Issues: Infertility or recurrent miscarriage (mainly with submucosal fibroids).
Diagnosis of Fibroids
Pelvic Ultrasound: The most common and non-invasive imaging technique used to detect fibroids. It can determine the size, location, and number of fibroids.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides a more detailed view of fibroids, including their exact size and position, and helps in planning treatment.
Hysteroscopy: A procedure in which a thin tube with a camera (hysteroscope) is inserted into the uterus to visually examine the interior and confirm the presence of submucosal fibroids.
Sonohysterography: An ultrasound procedure that involves injecting sterile saline into the uterus to improve the visualization of fibroids during the scan.
Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure used in some cases to assess the uterus and fibroids, especially if they are suspected to be outside the uterus.
Treatment Options for Non-Cancerous Fibroids
Treatment of fibroids depends on factors such as the severity of symptoms, size and location of the fibroids, and the woman’s desire to maintain fertility. Options range from watchful waiting to surgical intervention.
1. Conservative Management (For Small, Asymptomatic Fibroids)
In many cases, fibroids do not require treatment, especially if they are small and asymptomatic. Regular monitoring with ultrasounds may be recommended to track their size. If fibroids do not cause significant symptoms or complications, a “watch and wait” approach is often sufficient.
Pain Management: Over-the-counter medications like NSAIDs (ibuprofen or naproxen) may be used to relieve mild pelvic discomfort or pain.
2. Medications for Symptom Management
a) Hormonal Treatments
Hormonal therapy is often the first-line approach to managing symptoms of fibroids, especially for those with heavy menstrual bleeding.
Birth Control Pills: Help to regulate periods and reduce bleeding.
Progestin Intrauterine Device (IUD): A hormonal IUD, like Mirena, can reduce heavy bleeding and provide long-term symptom relief without affecting fertility.
GnRH Agonists (Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Agonists): Medications like leuprolide (Lupron) can shrink fibroids by temporarily lowering estrogen levels, effectively putting the body into a temporary menopausal state. These are typically used as a short-term solution before surgery or as a way to reduce symptoms.
Progestin Pills or Injections: These can help reduce bleeding but are less commonly used for long-term treatment.
b) Non-Hormonal Medications
Tranexamic Acid: A medication that helps reduce heavy bleeding by promoting clotting.
NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): These medications help to relieve pelvic pain associated with fibroids.
3. Minimally Invasive Procedures
a) Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE):
Purpose: A non-surgical procedure that blocks the blood supply to the fibroids, causing them to shrink.
Procedure: Small particles are injected into the blood vessels supplying the fibroids via a catheter inserted through the groin.
Indications: Suitable for women who do not want surgery or are looking to preserve their uterus, especially if they have large or multiple fibroids.
Benefits: Minimally invasive with a short recovery time.
b) MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound (MRgFUS):
Purpose: Uses high-frequency ultrasound waves to heat and destroy fibroid tissue.
Procedure: Performed under MRI guidance to accurately target the fibroids while leaving surrounding tissue unharmed.
Indications: Non-invasive, suitable for women who do not wish to undergo surgery, but requires specific fibroid types and locations.
4. Surgical Options
If symptoms are severe or other treatments fail, surgical options may be considered. Surgical management also depends on whether a woman wishes to preserve her fertility.
a) Myomectomy:
Purpose: Surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus.
Procedure: Can be done through:
Abdominal Myomectomy: An open surgery through an abdominal incision.
Laparoscopic Myomectomy: A minimally invasive option using small incisions and a camera.
Hysteroscopic Myomectomy: Suitable for submucosal fibroids, done through the vagina with a hysteroscope.
Indications: Recommended for women who wish to retain fertility and avoid hysterectomy.
b) Hysterectomy:
Purpose: Removal of the uterus.
Procedure: This is a definitive solution for fibroid treatment, often recommended for women who have completed their family or for those with severe symptoms that do not respond to other treatments.
Total Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus and cervix.
Subtotal Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus, leaving the cervix intact.
Indications: Most often recommended for women with large fibroids, severe symptoms, or who have completed childbearing.
5. Alternative Treatments
Some women explore complementary therapies such as acupuncture, herbal treatments, or dietary changes. While these may provide symptom relief, they should be used in conjunction with conventional medical treatments and after consultation with a healthcare provider.
6. Post-Treatment Care
Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-ups after treatment are essential to monitor for recurrence of fibroids or any new complications.
Pregnancy After Treatment: Women who undergo a myomectomy should consult their healthcare provider about fertility outcomes and any possible complications during pregnancy.
Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight and regular exercise can reduce the risk of fibroid growth and improve overall reproductive health.
Conclusion
Non-cancerous fibroids are a common concern for many women, and treatment options vary depending on the symptoms, size, and location of the fibroids. Early diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan can help manage symptoms effectively and preserve fertility. Women experiencing fibroid-related symptoms should consult a gynecologist for appropriate diagnosis and management tailored to their individual needs.
Empower
Your Health, Your Power
Prevention begins with awareness. By choosing proactive care, you’re taking charge of your health today—for a stronger, healthier tomorrow.
